
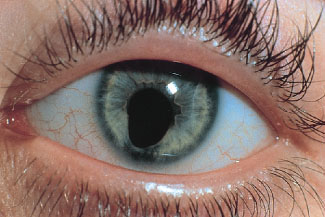
The repair process is by pupilloplasty with an internal Siepser sliding knot. In these cases, if the patient is symptomatic, surgical repair can be performed at the time of the cataract surgery. Given as an example, a case with an iris sphincter tear a superior iridodialysis, which is defined as separation of the iris from its attachment to the ciliary body, and a traumatic cataract.ĭiffuse dilation also can occur following trauma. Traumatic mydriasis can result from open or closed globe injuries. Iris Reconstruction – Traumatic Mydriasis An important point in such cases is to avoid inadvertent incarceration of the iris into the suture as well as to avoid cutting the iris, except in cases in which it is frankly necrotic or epithelialized because the iris tissue can be used for future reconstruction. Injecting excessive viscoelastic can result in increased pressure and additional iris prolapse. In cases of open globe injuries when there is iris prolapse, it is good to make a paracentesis opposite to the area of the prolapse this is followed by injection of a minimal amount of a viscoelastic and gentle repositioning of the iris using an iris sweep. Abnormalities of pupil size, shape and location may also be reasons for pupil reconstruction. In addition, cosmetic issues are often present, especially when a patient has a light-colored iris. Other symptoms include reduced visual acuity and contrast sensitivity loss.
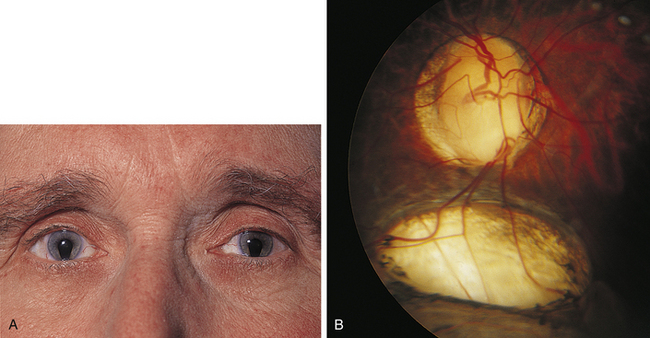
The visual dysfunction may vary from mild to severe. Patients in need of such reconstructive efforts, either in cases of congenital, traumatic or other causes of iris loss, often are significantly debilitated by light and glare sensitivity, as well as other visual disturbances resulting from a compromised iris diaphragm. Iris reconstructive surgery is among the most difficult operations performed by the anterior segment surgeon, especially after ocular trauma. Alternatively, the artificial iris can be placed inside the “bag” in a combined procedure with cataract surgery. This artificial iris can be sutured to the wall of the eye (sclera) in front of the “bag” that holds the lens, a region called the sulcus. Iris prosthetics involves inserting a custom made artificial iris that is carefully matched to the color of the other eye. If the iris is so badly damaged that it cannot be repaired, an iris prosthesis can be used. Sometimes the surgeon may cut some of the existing iris to help improve the appearance. Iris repair often involves the use of sutures inside the eye to reshape the iris to its original shape, re-creating a round pupil.

Iris surgeries come in the form of iris repair (iridoplasty) or an iris prosthesis. Patients may also be concerned about the appearance of their eye, and wish for repair for aesthetic reasons. Symptoms of iris conditions are usually secondary to the amount of light that enters the eye, and patients typically report light sensitivity (photophobia) due to excessive light exposure. In these types of cases, the surgeon may offer a form of iris surgery to the patient. In some cases, patients are born with defects in their iris, and other inherited conditions may even involve absence of the iris. Sometimes, the iris (the colored part of the eye that forms the pupil) may be damaged, as can occur with trauma or previous surgery. The iris - the colored part of the eye - is a ring of muscle and connective tissue fibers that contract and expand to open and close the pupil in response to the brightness of surrounding light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
